State Government Resources
Links to other state government agency and organization websites.
Governor's Cabinet in Your Community
Governor's Cabinet in Your Community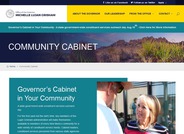
A state government-wide constituent services outreach day. For the first (and not the last!) time, key members of the Lujan Grisham administration will make themselves available to members of every New Mexico community for a wide variety of constituent service needs. Cabinet leaders, constituent services personnel from various state agencies and Governor’s Office staff will be on hand to field walk-in requests and phone correspondence. Constituents can expect a helping hand and direct assistance from state government, because this government works for you! |
Governor's Commission on Disability
Governor's Commission on Disability
Governor's Commission on Disability |
Group A Streptococcal Disease Information for Clinicians
Group A Streptococcal Disease Information for Clinicians
Group A streptococcal disease information for clinicians including clinical features, etiologic agent, incidence, sequelae, transmission, risk groups, surveillance, and more. |
Group A Streptococcus Report 2011
Group A Streptococcus Report 2011
Active Bacterial Core Surveillance personnel routinely contacted all microbiology laboratories serving acute care hospitals in their area to identify cases. Standardized case report forms that include information on demographic characteristics, clinical syndrome, and outcome of illness were completed for each identified case. Strains were emmtyped at the Centers for Disease Control. Regular laboratory audits assessed completeness of active surveillance and detected additional cases. |
Group B Streptococcus Report 2011
Group B Streptococcus Report 2011
Active Bacterial Core Surveillance personnel routinely contacted all microbiology laboratories serving acute care hospitals in their area to identify cases. Standardized case report forms that include information on demographic characteristics, clinical syndrome, and outcome of illness were completed for each identified case. Regular laboratory audits assessed completeness of active surveillance and detected additional cases. |
Guardianship Program
Guardianship Program
The purpose of this website is to promote advocacy, capacity building, and systemic change to improve the quality of life for individuals with developmental disabilities and their families. |
Guidelines for the Prevention of Perinatal Group B Streptococcal Disease 2010
Guidelines for the Prevention of Perinatal Group B Streptococcal Disease 2010
Revised Guidelines for the Prevention of Perinatal Group B Streptococcal Disease were published in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report on November 19, 2010. These 2010 guidelines were developed using an evidence-based approach in collaboration with several professional associations. |
Guillain-Barré Syndrome During the 2009–2010 H1N1 Influenza Vaccination Campaign: Population-based Surveillance Among 45 Million Americans
Guillain-Barré Syndrome During the 2009–2010 H1N1 Influenza Vaccination Campaign: Population-based Surveillance Among 45 Million Americans
Because of widespread distribution of the influenza A (H1N1) 2009 monovalent vaccine (pH1N1 vaccine) and the prior association between Guillain-Barre´ syndrome (GBS) and the 1976 H1N1 influenza vaccine, enhanced surveillance was implemented to estimate the magnitude of any increased GBS risk following administration of pH1N1 vaccine. The authors conducted active, population-based surveillance for incident cases of GBS among 45 million persons residing at 10 Emerging Infections Program sites during October 2009–May 2010; GBS was defined according to published criteria. |
Haemophilus influenzae Disease Information for Clinicians
Haemophilus influenzae Disease Information for Clinicians
Haemophilus influenzae disease information for clinicians including clinical features, sequelae, etiologic agent, transmission, risk groups, incidence, trends, and more. |
Haemophilus influenzae Type B Information
Haemophilus influenzae Type B Information
Haemophilus influenzae is a cause of bacterial infections that are often severe, particularly among infants. It was first described by Pfeiffer in 1892. During an outbreak of influenza he found the bacteria in sputum of patients and proposed a causal association between this bacterium and the clinical syndrome known as influenza. The organism was given the name Haemophilus by Winslow, et al. in 1920. It was not until 1933 that Smith, et al. established that influenza was caused by a virus and that H. influenzae was a cause of secondary infection. |
Harm Reduction Regulation Hearing-20220817_090010-Meeting Recording
Harm Reduction Regulation Hearing-20220817_090010-Meeting Recording
Harm Reduction Regulation Hearing-20220817_090010-Meeting Recording |
HB52 Advocate Interview
HB52 Advocate Interview
HB52 Advocate Interview |


