Substance Use Epidemiology Section
Welcome to the website for the Substance Use Epidemiology Section (SUES). SUES collects and analyzes data on substance use in New Mexico and shares the results with community groups, policy makers, and other stakeholders. Examples of substance abuse data that SUES assesses include alcohol-related death, drug overdose death, excessive alcohol consumption, and naloxone distribution.
There are other programs within the Department of Health that also work to prevent negative health outcomes due to substance use. If you are looking for information about preventing prescription opioid overdose, please visit the Opioid Safety & Overdose Prevention section of our website. If you are looking for information about harm reduction, including naloxone distribution and syringe services for people who are injecting drugs, please visit the Harm Reduction section of our website. If you are looking for information about tobacco use prevention and cessation, please visit the Nicotine Use Prevention and Control Program section of our website. If you are looking for information about decreasing alcohol-related harms and deaths, please visit the Office of Alcohol Misuse Prevention section of our website.
Additionally, SUES maintains a number of Substance Use Epidemiology Data Reports on New Mexico’s Indicator-Based Information System website and SUES maintains the Substance Use & Mental Health Epidemiology Profile (SUMHEP) Dashboard.
Recent Activity
Health Data
Featured
- Recent Drug Overdose Data Trends: Doña Ana County, Rio Arriba County, Santa Fe County, Taos County, and New Mexico, 2021-2025 (Substance Use) (Substance Use)
- New Mexico Substance Use State Epidemiology Profile 2024 (August - Corrected) (Substance Use)
- Alcohol Screening and Brief Intervention New Mexico, 2014 (Epidemiology Report)
Latest
- Northeast Monthly Substance Use Report September 2025 (Substance Use)
- Northwest Monthly Substance Use Report September 2025 (Substance Use)
- Southeast Monthly Substance Use Report September 2025 (Substance Use)
Popular
- Drug Abuse Patterns and Trends in New Mexico (September 2004) (Substance Use)
- New Mexico Substance Use State Epidemiology Profile 2018 (December) (Substance Use)
- New Mexico Substance Use State Epidemiology Profile 2020 (January) (Substance Use)
Publications
Featured
- Alcohol Use in New Mexico Infographic (October 2025) (Marketing)
- Alcohol Use in McKinley County (June 2023) (Marketing)
- Alcohol Outlet Density in New Mexico Infographic (February 2016) (Marketing)
Latest
- Substance Use & Mental Health Epidemiology Profile Dashboard - Executive Summary (September 2025) (General)
- Substance Use & Mental Health Epidemiology Profile Dashboard - Introduction (September 2025) (General)
- DOSE Digest – Published by the CDC OD2A Team (March 2025) (Marketing)
Popular
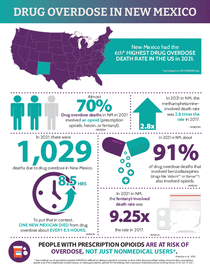
- Drug Overdose in New Mexico Infographic (May 2022) (Marketing)
- Prescription Monitoring Infographic (March 2016) (Marketing)
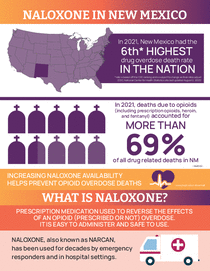
- Naloxone in New Mexico Infographic (May 2022) (Marketing)
Substance Use and Related Reports
Region-Specific Syndromic Surveillance Reports
- Northeast - Northeast Monthly Substance Use Report September 2025
- Northwest - Northwest Monthly Substance Use Report September 2025
- Southeast - Southeast Monthly Substance Use Report September 2025
- Southwest - Southwest Monthly Substance Use Report September 2025
Reports
- Birth Defects Surveillance in NM 2015 - 2024
- 2024 - New Mexico Substance Use State Epidemiology Profile 2024 (August - Corrected)
- 2022 - New Mexico Substance Use State Epidemiology Profile 2022 (August)
- 2021 - New Mexico Substance Use State Epidemiology Profile 2021 (February)
- 2020 - New Mexico Substance Use State Epidemiology Profile 2020 (January)
Infographics
Alcohol-Related
Infographics
Learn More
Indicator-Based Information System (NM)-(IBIS)
- Alcohol-Related Chronic Disease Deaths
- Alcohol-Related Death
- Alcohol-Related Injury Deaths
- Drug Overdose Deaths
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
- DOSE-SYS Dashboard: Nonfatal Overdose Syndromic Surveillance Data
- Preventing Excessive Alcohol Consumption
- Unintentional Poisonings
- Persons Who Use Drugs
National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism
- National Institute on Drug Abuse
- National Institute of Mental Health
Others
Substance Use-Related Publications
Sacks JJ, Gonzales KR, Bouchery EE, Tomedi LE, Brewer RD. (2015) 2010 National and State Costs of Excessive Alcohol Consumption. American Journal of Preventive Medicine, 49(5):e73-9.
Landen MG, Castle S, Nolte KB, Gonzales M, Escobedo LG, Chatterjee BF, Johnson K, Sewell CM. (2003) Methodological issues in the surveillance of poisoning, illicit drug overdose and heroin overdose deaths in New Mexico. American Journal of Epidemiology, 57(3): 273-278.
Shah N, Lathrop SL & Landen MG. (2005) Unintentional methadone-related overdose death in New Mexico (USA) and implications for surveillance, 1998-2002. Addiction, 100(2), 176-188.
Mueller MR, Shah N & Landen MG. (2006) Unintentional prescription drug overdose deaths in New Mexico, 1994–2003. American Journal of Preventive Medicine, 30(5), 423-429.
Woerle S, Roeber J, Landen MG. (2007) Prevalence of alcohol dependence among excessive drinkers in New Mexico. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research, 31(2), 293-298.
Shah N, Lathrop SL, Reichard RR & Landen MG. (2008) Unintentional drug overdose death trends in New Mexico (USA), 1990-2005: combinations of heroin, cocaine, prescription opioids and alcohol. Addiction, 103(1), 126-36.
Stahre M, Roeber J, Kanny D, Brewer RD, Zhang X. (2014) Contribution of excessive alcohol consumption to deaths and years of potential life lost in the United States. Prev Chronic Dis, 26;11:E109.
Landen M, Roeber J, Naimi T, Nielsen L, Sewell M. (2014) Alcohol-attributable mortality among American Indians and Alaska Natives in the United States, 1999-2009. Am J Public Health, 104 Suppl 3:S343-9.
Substance Use-Related MMWRs
CDC (2005) Unintentional deaths from drug poisoning by urbanization of area – New Mexico, 1994-2003. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, 54(35), 870-874.
CDC (2007) Types of alcoholic beverages usually consumed by students in 9th-12th grades--four states, 2005. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, 56(29), 737-740.
Gonzales K, Roeber J, Kanny D, Tran A, Saiki C, Johnson H, Yeoman K, Safranek T, Creppage K, Lepp A, Miller T, Tarkhashvili N, Lynch KE, Watson JR, Henderson D, Christenson M, Geiger SD; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2014) Alcohol-attributable deaths and years of potential life lost--11 States, 2006-2010. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, 63(10), 213-6.